Introduction to Tenses
When we are reading anything, how do we know if the events are happening in the past, present or the possible future? In grammar, we indicate time by modifying the verbs accordingly. Let us see how this is done in Introduction to Tenses.
Introduction to Tenses
In English grammar, verbs are often used in a way that it indicates or denotes the time when an event occurred. These verbs that take up different forms to indicate the time of an action, event or condition by changing its form are called as tenses. Tenses can be broadly classified into three broad categories:
- Past Tense
- Present Tense
- Future Tense
With each of these tenses, there are four aspects associated with it. An aspect here refers to the nature of action performed by the verb. We will also learn about them in an introduction to tenses.
- Perfect or complete
- Perfect continuous
- Progressive or Continuous
- Simple or indefinite.
This way, we get total possibilities of 12 tenses in English grammar. Let us understand more about each of these groups of tenses.
(Source: pineterst)
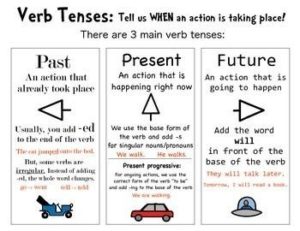
Past, Present & Future
Past Tense
This tense is used to refer to something that happened in the past. Sometimes, past tense is also called as ‘simple past tense’. Example: We stayed in a hotel.
- Past continuous tense: This type of past tense is used to describe an event or occurrence that is ongoing or continuing in the past. Example: We were playing tennis at the club.
- Past Perfect Tense: This type of tense is used to describe an event in the past that has been completed. Example: We had completed our match before she had come.
- Past Perfect Continuous: This type of past tense verb is used to indicate an event, action or occurrence that started before another event, action or occurrence in the past. We can say that one action or event interrupted another. Example: I had been playing the drums since school time.
Learn more about Uses of Past Tense here in detail.
Present Tense
This tense is used to refer or indicate to something that occurs in the present. The simple present or indefinite present tense is used to describe an action, event, or condition that is occurring in the present while being spoken about or written. Example: The dogs’ bark.
- Present Continuous Tense: This tense indicates the continuous nature of an act or event in the present and has not been completed. The activity has begun in the past and will be completed in the future. Example: She is preparing chicken sandwiches for breakfast.
- Present Perfect Tense: This tense is used to describe an action that had begun in the past, continues into the present and has just been completed. The time of occurrence of the action is generally not mentioned. This tense is also used to describe an action happened in the past before another action took place. Example: I have just completed my dinner.
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe an action, event or occurrence that has begun in the past and continues into the present. It is also used for an action that began and just finished in the past or in cases where there is no mention of time. Example: They have been trying to contact her.
Learn more about Sequences of Tenses here in detail.
Future Tense
This tense is used to refer to or indicate something that hasn’t happened at the time of speaking or writing. ‘Simple Future Tense’ commonly formed with the use of words ‘will’ and ‘shall’. Example: We shall be there by noon.
- Future Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe actions that are ongoing or continuing in the future. It is commonly used in sentences by using the simple future tense of the verb with the present participle i.e ‘-ing’. Example: His parents will be attending the convocation.
- Future Perfect Tense: Is used to refer or describe an event that will be completed sometime in the future before another action takes place. It is written by using the past participle of the verb with the simple future tense of the verb. Example: I will have completed 10 years of work in August this year.
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense: This tense is used to describe an action that is continuing into the future and will be completed at a specified time in the future. This tense is written using the future perfect tense of the verb with the present participle. Example: I shall have been living in Mumbai for five years by May 2019.
With this introduction to tenses, you may have now got a good idea about the tenses and their various types and forms. We will learn more about each of these tenses in the following chapters.
Learn the rules for changing tenses between Active Voice and Passive Voice.
Solved Example for You
Q. She _________ food when the guests arrived yesterday.
a.) preparing b.) was preparing
c.) is preparing d.) has been preparing
Sol. (b) was preparing. The sentence is in past tense which is indicated by the word ‘yesterday’. It is also indicated in the sentence that it is in past continuous tense due to the words ‘when the guests arrived’.
So, the option which is indicative of past continuous tense is option b) was preparing. The completed sentence is: She was preparing food when the guests arrived yesterday.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Welcome